Inheritance
Scala offers the single class inheritance, which means a class can only inherit ONE class.
Constructor
JVM initializes the parent class before the current class.
class Person(name: String)
class Adult(name: String, job: String) extends Person(name)
Override
class Animal {
protected def eat = println("nom nom")
}
class Dog extends Animal {
override def eat = println("crunch crunch")
}
Dog overrides the method eat from its parent class Animal.
We can also prevent override.
-
add
finalto the class member (attribute or method) so that it can't be overrided by derived classes.class Animal { final def eat = println("nom nom") } -
add
finalto the class itself so that the class can't be inherited.final class Animal -
sealedthe class so that it can ONLY be inherited by the classes in the same file.sealed class Animal
Polymorphism
val pet: Animal = new Dog
In this case, pet is an instance of Dog although we declare it as an Animal.
Abstract class
abstract class Animal {
val type: String
def eat: Unit
}
In this abstract class, both the attribute and the method are not defined. We can let sub-classes to implement them.
Of course, we can put non abstract member to an abstract class.
abstract class Animal {
val type: String
def eat = println("nom nom")
}
Traits
Since Scala class can ONLY inherit ONE class, we create trait to make it extend multiple traits.
Therefore, trait is same to abstract class, which can have both abstract and non abstract member.
abstract class Animal
trait Flying
trait Eating
class Bird extends Animal with Flying with Eating
Type Hierarchy
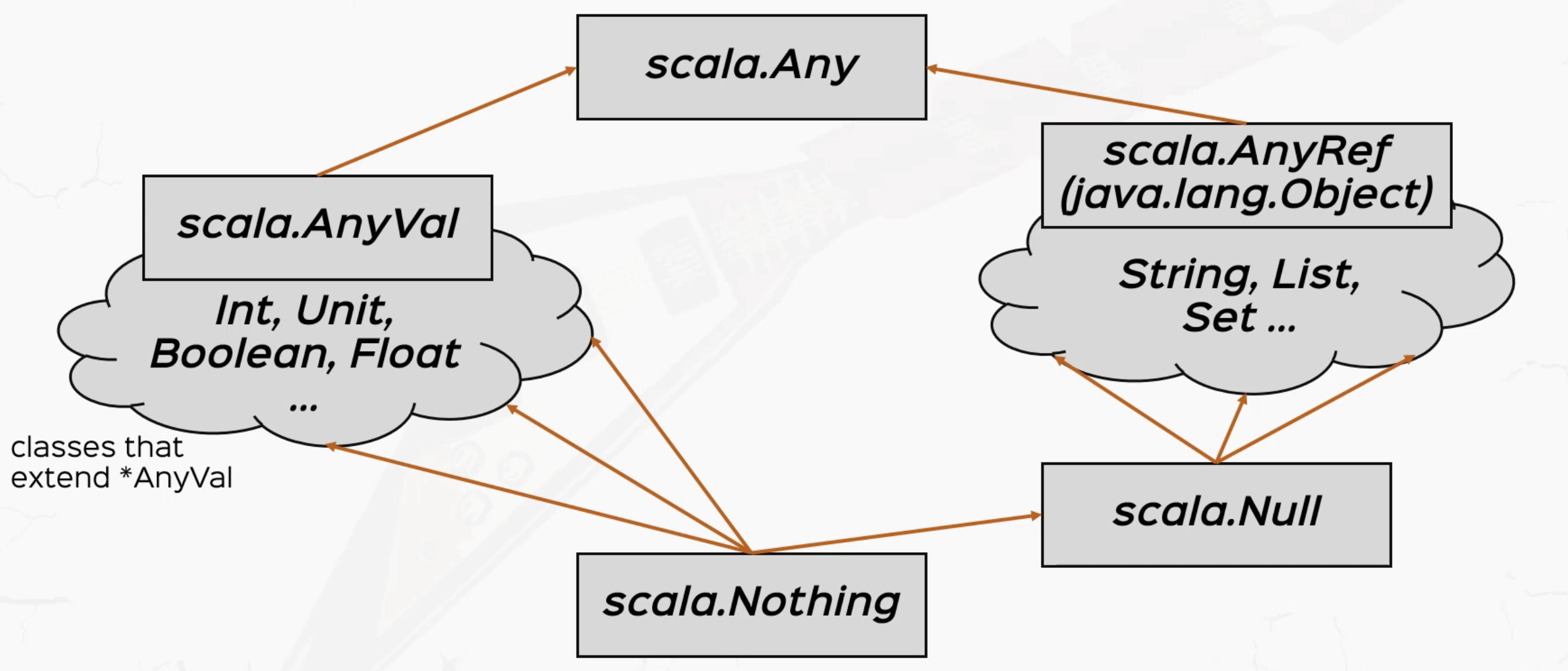
-
Anyis the root class. -
AnyRefandAnyValinheritAny-
AnyRefcontains the classes fromJava.lang.Object, such asString,List,Set, etc.Nullinherit it. -
AnyValcontains primitive classes, such asInt,Boolean,Float,Unit, etc.
-
-
Nothinginherits all the classes in Scala.
var a: Int = ??? // It means Nothing.
Anonymous class
class Person(val name: String) {
def greet = println(s"I'm $name.")
}
val jack = new Person("Jack") {
override def greet = println(s"My name is $name.")
}
In this case, Scala will create an anonymous class that inherits the class Person and instantiate it.