Dependencies
The rule of thumb tries to determine when a shuffle might occur.
Rule of thumb: A shuffle can occur when the resulting RDD depends on other elements from the same RDD or another RDD.
Transformations can have two kinds of dependencies:
-
Narrow dependencies
Each partition of the parent RDD is used by at most one partition of the child RDD.
It's fast. No shuffle necessary.
-
Wide dependencies
Each partition of the parent RDD is used by multiple partitions of the child RDD.
It's slow. Requires all or some data to be shuffled over the network.
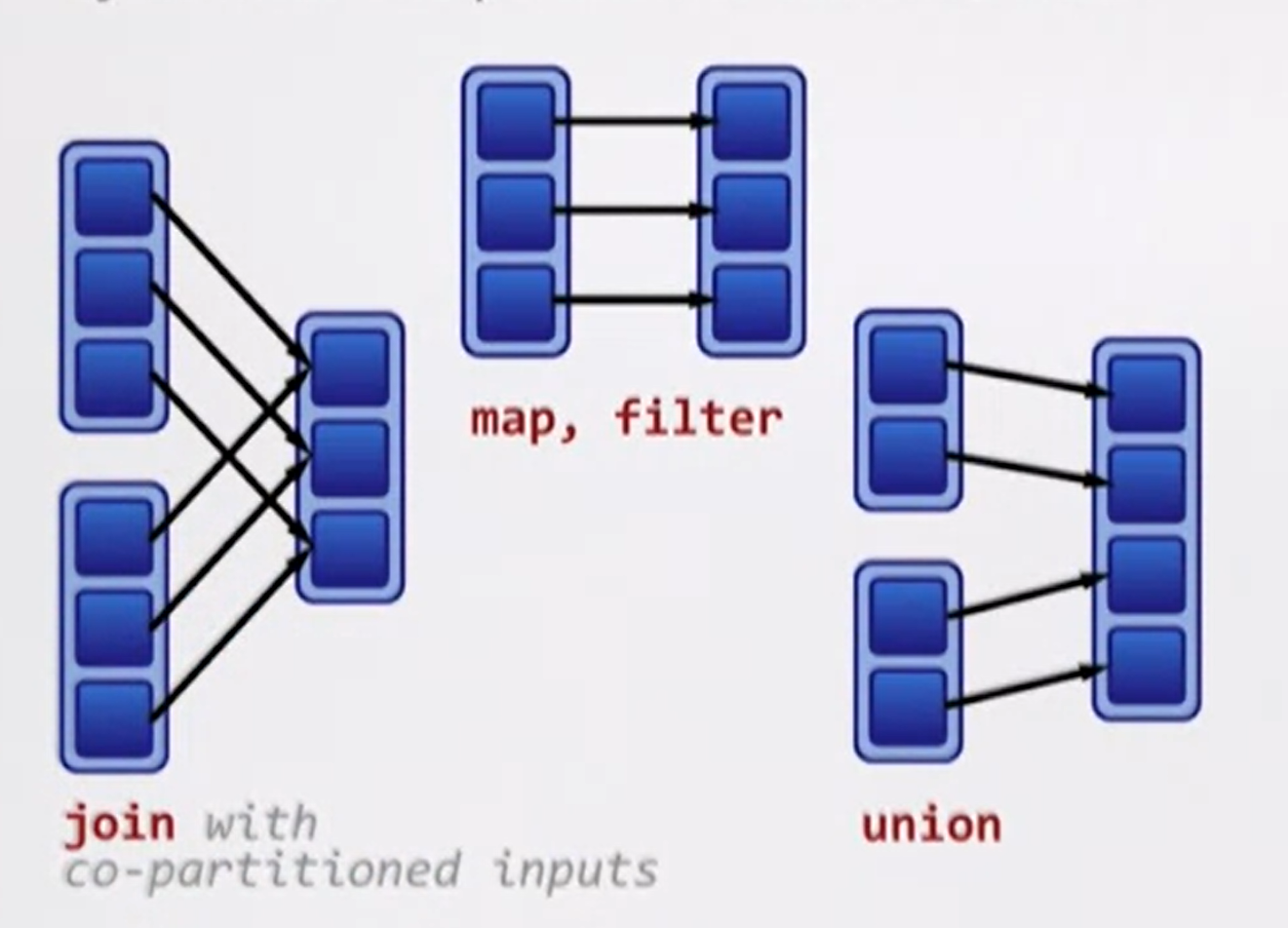
Narrrow dependencies
-
map -
union -
join
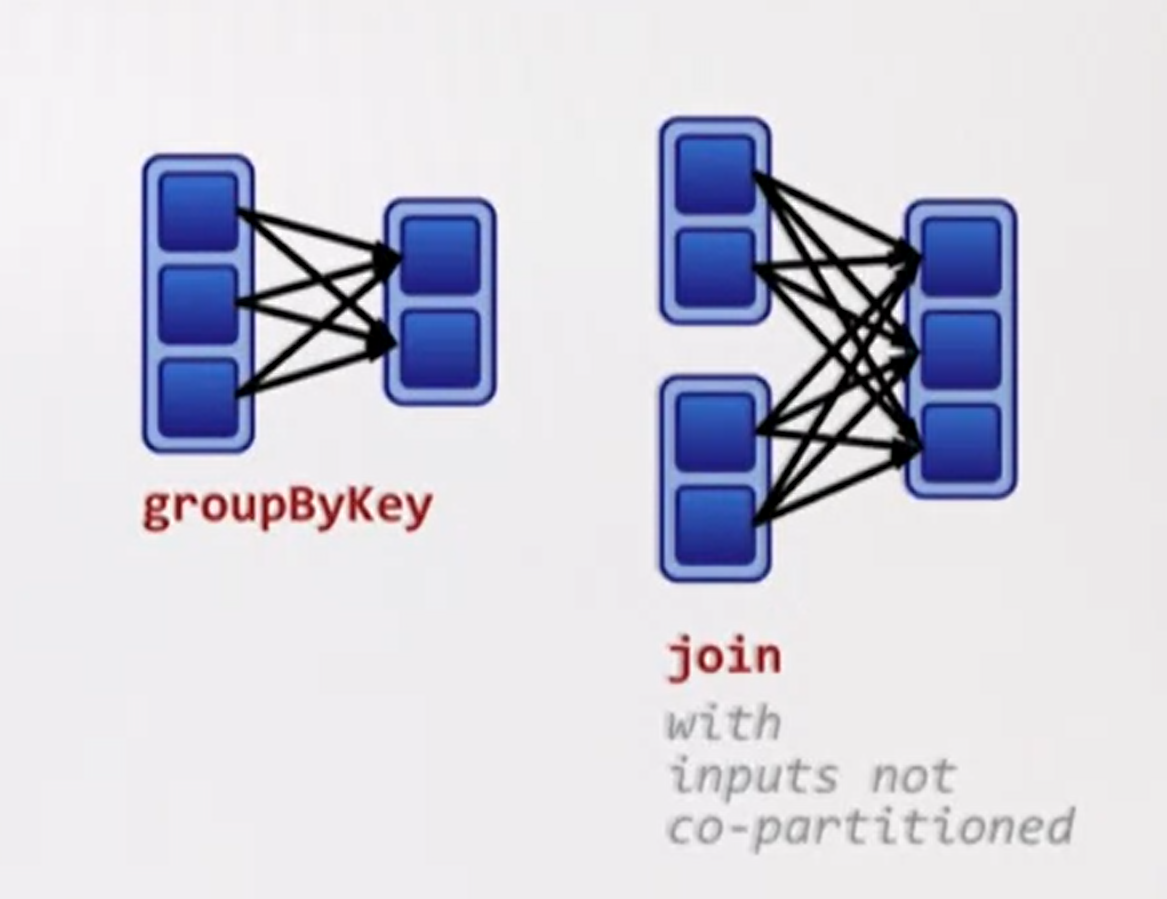
Wide dependencies
-
groupBy -
join
How can I find out the type of dependencies ?
dependencies or toDebugString method on RDDs.
-
Narrow dependency objects
- OneToOneDependency (commonly seen)
- PruneDependency
- RangeDependency
-
Wide dependency objects
- ShuffleDependency
Fault tolerance
Lineages graph is the key to the fault tolerance in Spark.
Tree is a lineage graph.
Ideas from functional programming enables fault tolerance in Spark:
-
RDD is immutable.
-
We use higher-order functions, such as
map, on the immutable data. -
A function for computing based on its parent RDDs is also a part of RDD's representation.