Concept
Node
A process of Elasticsearch. It's recommended to lanuch only one process per server.
-
Coordinating Node: The node that processes the request. It proxies the requests to the correct nodes. All the nodes are this kind of node by default.
-
Data Node: The node that saves data. The node is data node by default. We can change that by
node.data: false. -
Master Node: The nodes that
- handle create/delete index
- decide the shard are set to which node
- maintain the cluster state
In a cluster, we usually create more than one master nodes. Each node works only as a master node.
In a cluster, there are multiply master eligible node. It could be elected as the master node if the current one doesn't work. The node is master eligible by default. We can change that by
node.master: false.
Cluster State
The cluster state includes:
- the info of all the nodes
- the info of all the indexes and their
settingandmapping - the routing of shards
Master eligible node
The nodes will ping each other, the node whose node id is the smallest will be elected as master node.
There is a classic problem of the distributed system, Split-brain.
If the node1 is out of connection, the node3 will be elected as a master. When node1 is back to connection, there are 2 master nodes.
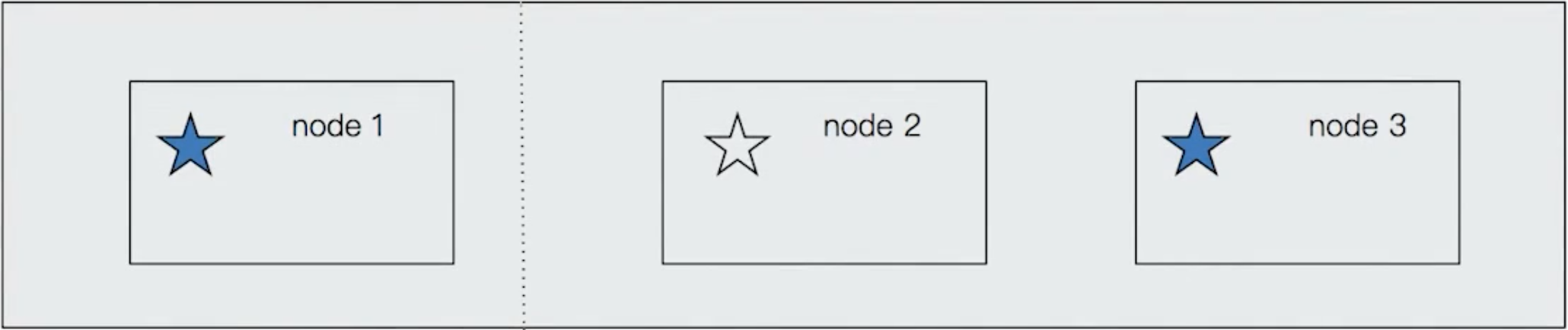
To avoid this problem, we should stop node1 to be elected as the master. Therefore, we can set a quorum. Only if the number of master eligible nodes is bigger than quorum, the election can take place.
quorum = (Total number of nodes / 2) + 1
Elasticsearch handled this for us.
Shard
There are 2 kinds of shard, primary shard and replica shard.
-
Primary shard
We can spread the data of an index on different data nodes for the horizontal scaling.
The primary shard is defined when creating an index, it can't be changed unless reindexing.
-
Replica Shard
It replicates the primary shard. It can be promoted as the primary shard when the primary one lost.
It also improves reading performance. However, too many replica shards will have a negative impact on writing performance.
With primary shard and replica shard, ES can handle the accident of nodes.
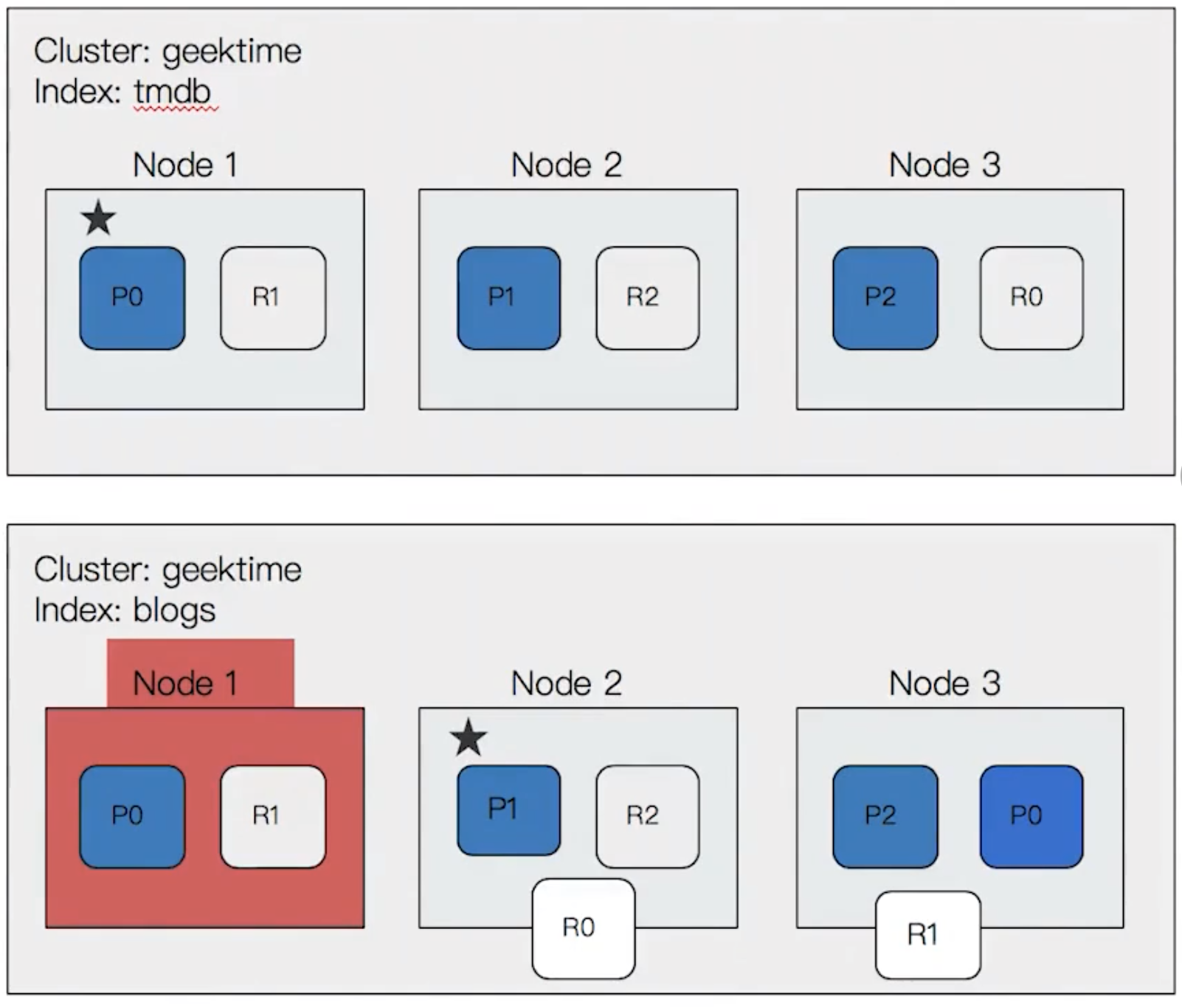
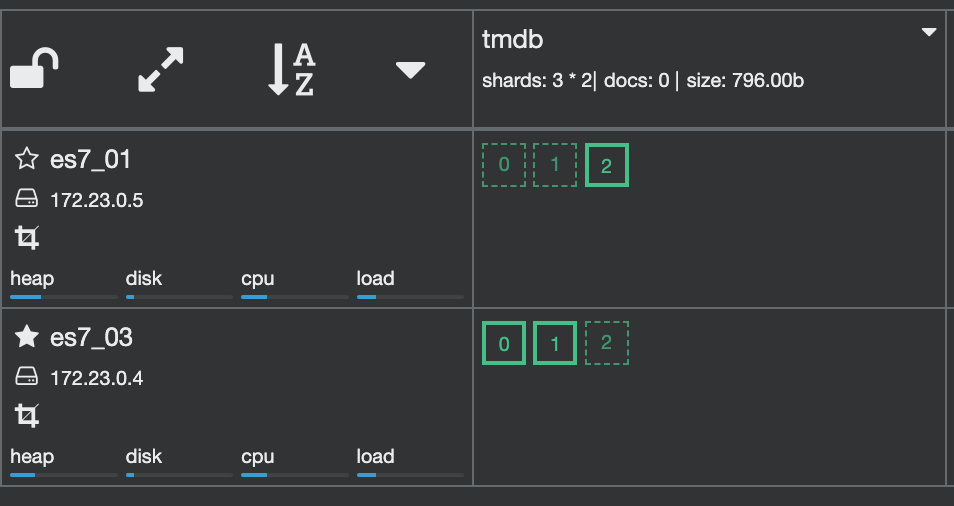
For example, here are the shards of an index tmdb.
PUT tmdb
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
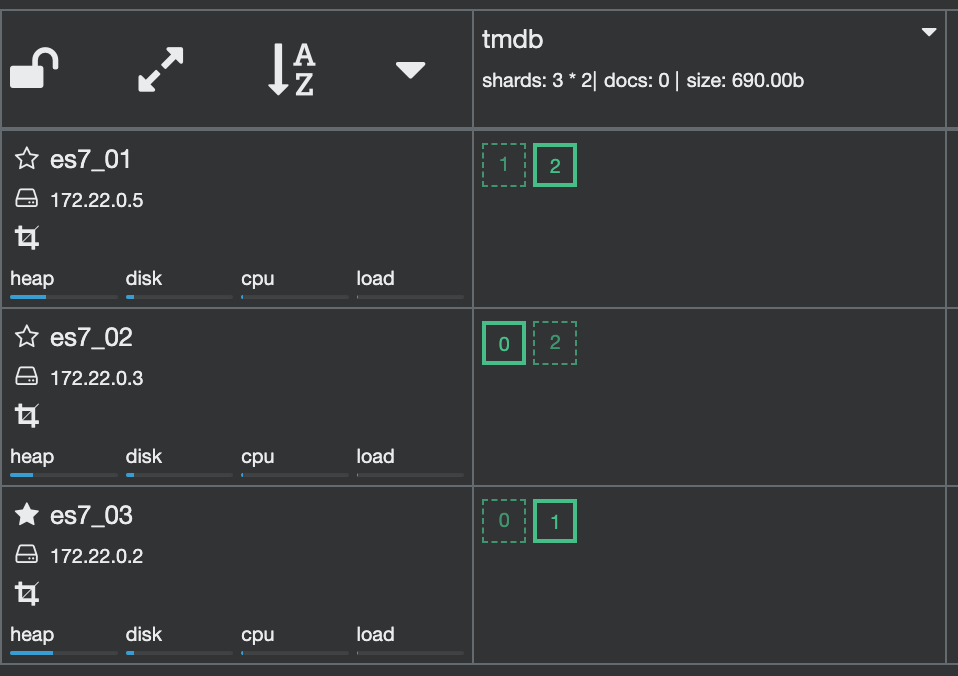
Now, if the node2 is down.
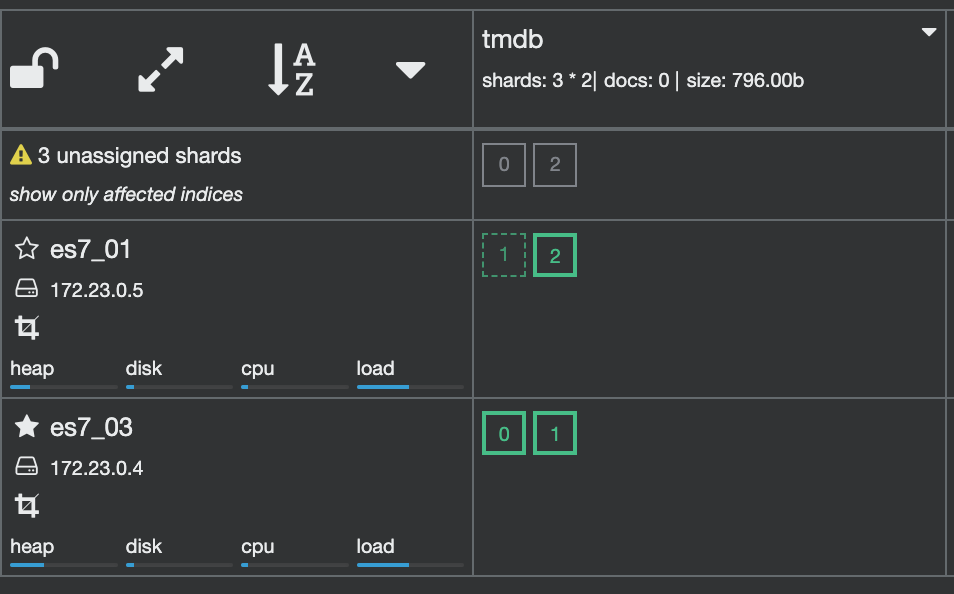
After a while, ES will relocate the shards.
Saving documents on shards
The shard that the document will be saved is calculated by:
shard = hash(_routing) % nb_of_primary_shard
The doc routing is id by default.
Refresh
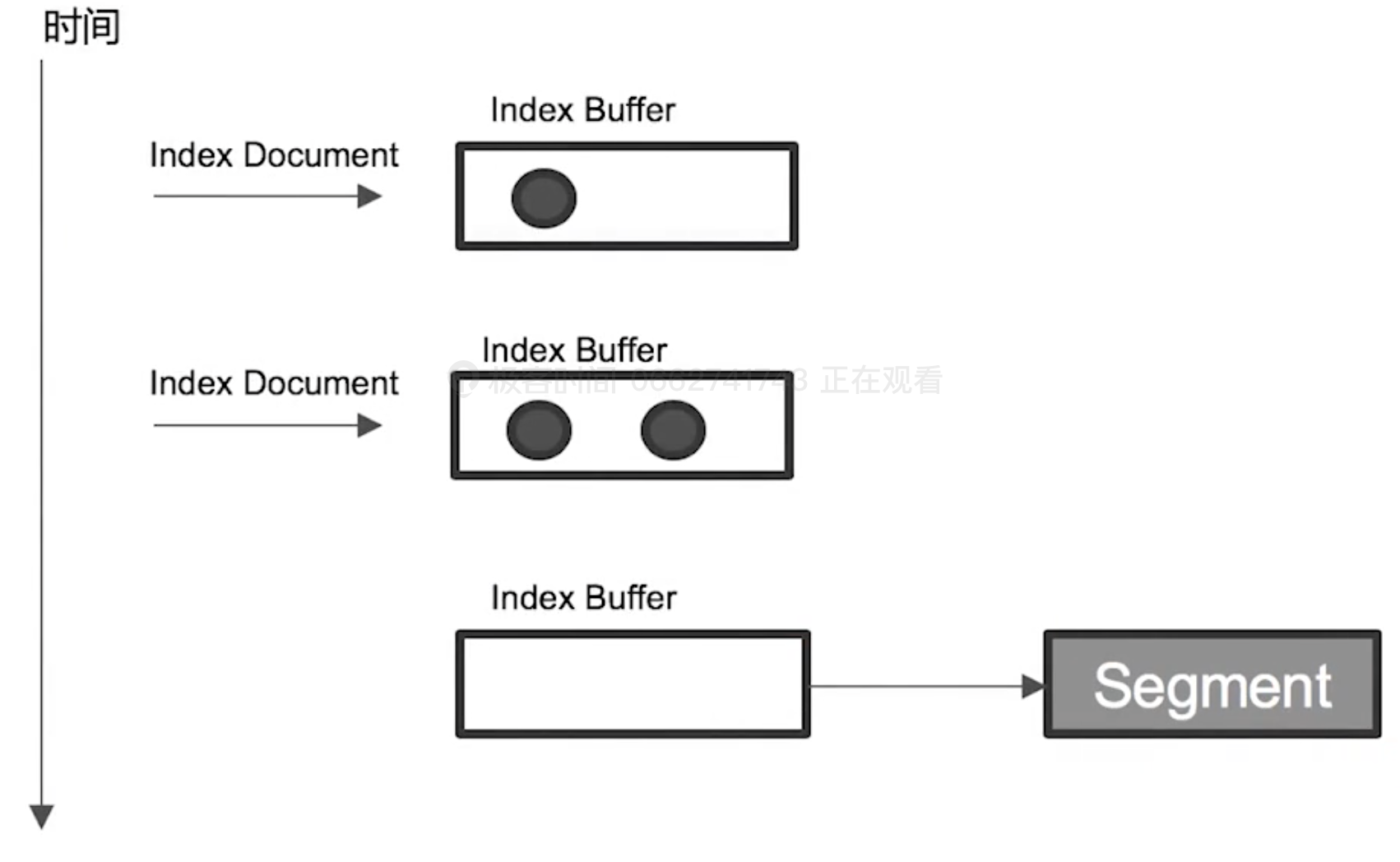
Refresh means writing data from the index buffer to the segment.
The collection of segments is a shard.
When there is a new doc is indexed, a new segment will be created.
Refresh freq: 1s
If the index buffer is full (10% of JVM), refresh will be triggered, too.
Transaction log
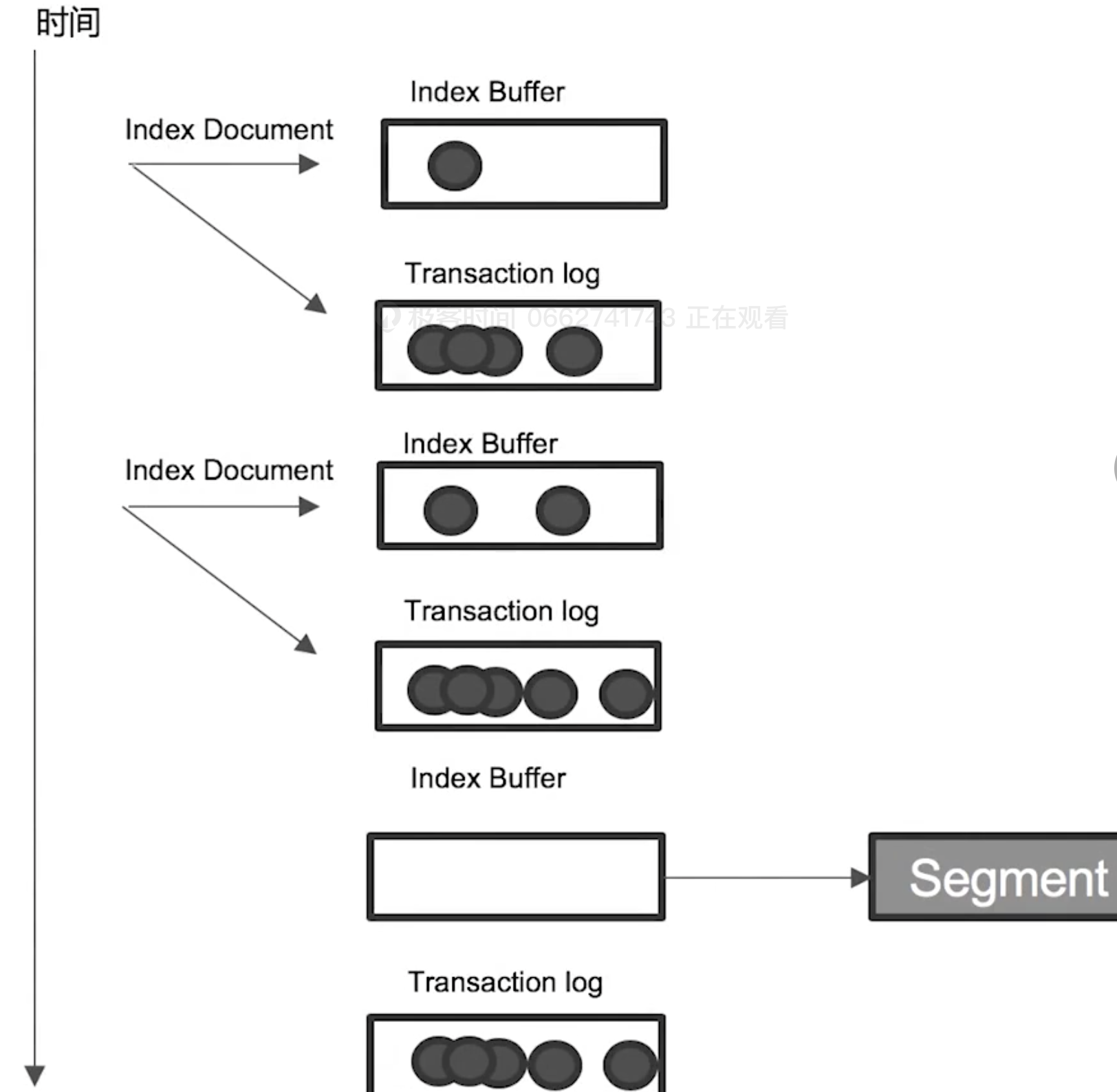
It costs time to write the segment to disks. To improve the performance, the segment is, first, written into the cache, and allow to be used for searching.
To keep the data when there is an accident (e.g. out of the electricity), the document will be written into the transaction log, and the transaction log is written into the disk.
After each refresh, the index buffer will be cleaned up. While the transaction log won't be.
Flush
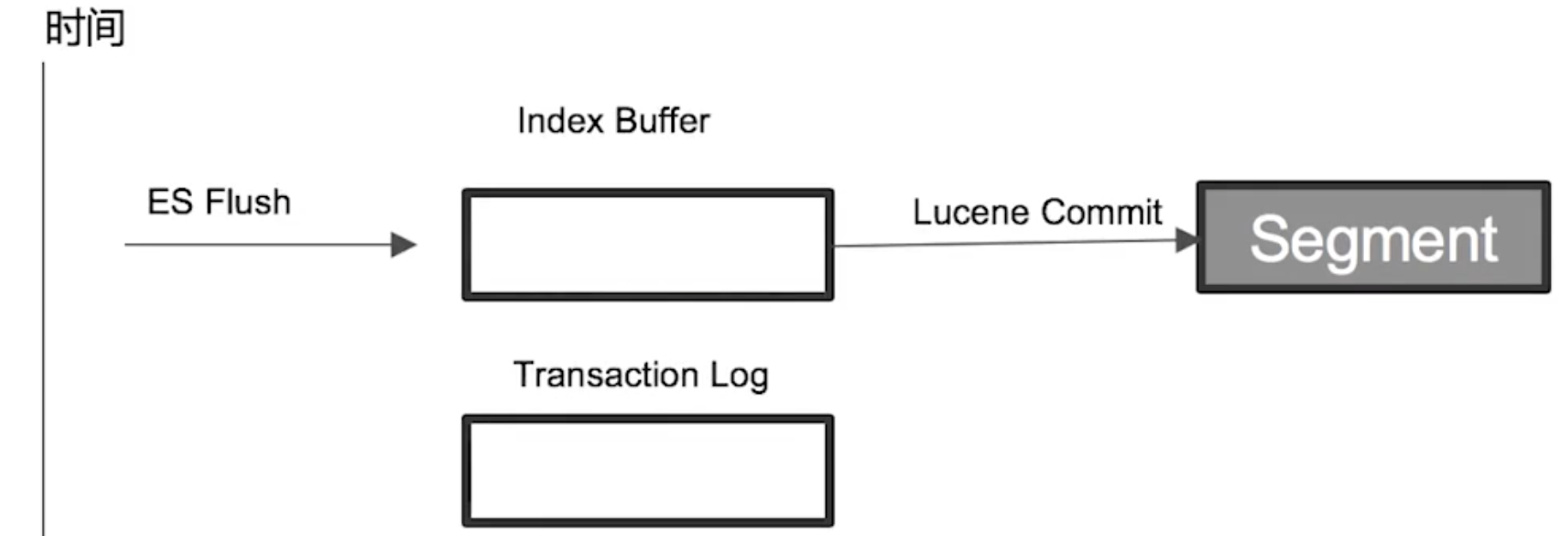
Flush will:
- clear the index buffers and transaction logs
- write the segments into disks
It will be triggered:
- every 30 min
- when the transaction log is full (512 MB)
Merge
It does 2 things:
- reduce the nb of segments
- delete removed documents