Aggregation
Aggregation is an attribute of Search API.
POST employees/_search
{
"size": 0 // Since we don't need the items
"aggs": {
"max_salary": {
"max": {
"field": "salary"
}
},
"min_salary": {
"min": {
"field": "salary"
}
},
}
}
Bucket
It can split the data into different buckets
POST employee/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"age_buckets": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 3
}
}
}
}
Nested aggregation
We can put an aggregation under another one.
POST employees/_search
{
"size": 0 // Since we don't need the items
"aggs": {
"job_buckets": {
"terms": {
"fields": "job.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"senior_employees": {
"top_hits": {
"size": 3,
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
Pipeline aggregation
Apply functions on the results of aggregation.
POST employees/_search
{
"size": 0 // Since we don't need the items
"aggs": {
"jobs": {
"terms": {
"fields": "job.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"avg_salary": {
"avg": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
}
},
"min_salary_by_jobs": {
"min_bucket": { // pipeline function
"bucket_path": "jobs>avg_salary" // bucket_path indicates it's a pipeline aggregation
}
}
}
}
Query + Aggregation
Query gives a range for aggregation result.
POST employees/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": { // the employee should be over 30 years old.
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"max_salary": {
"max": {
"field": "salary"
}
},
"all": {
"global": {} // It overrides the query range.
"aggs": {
"max_salary": {
"max": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Performance
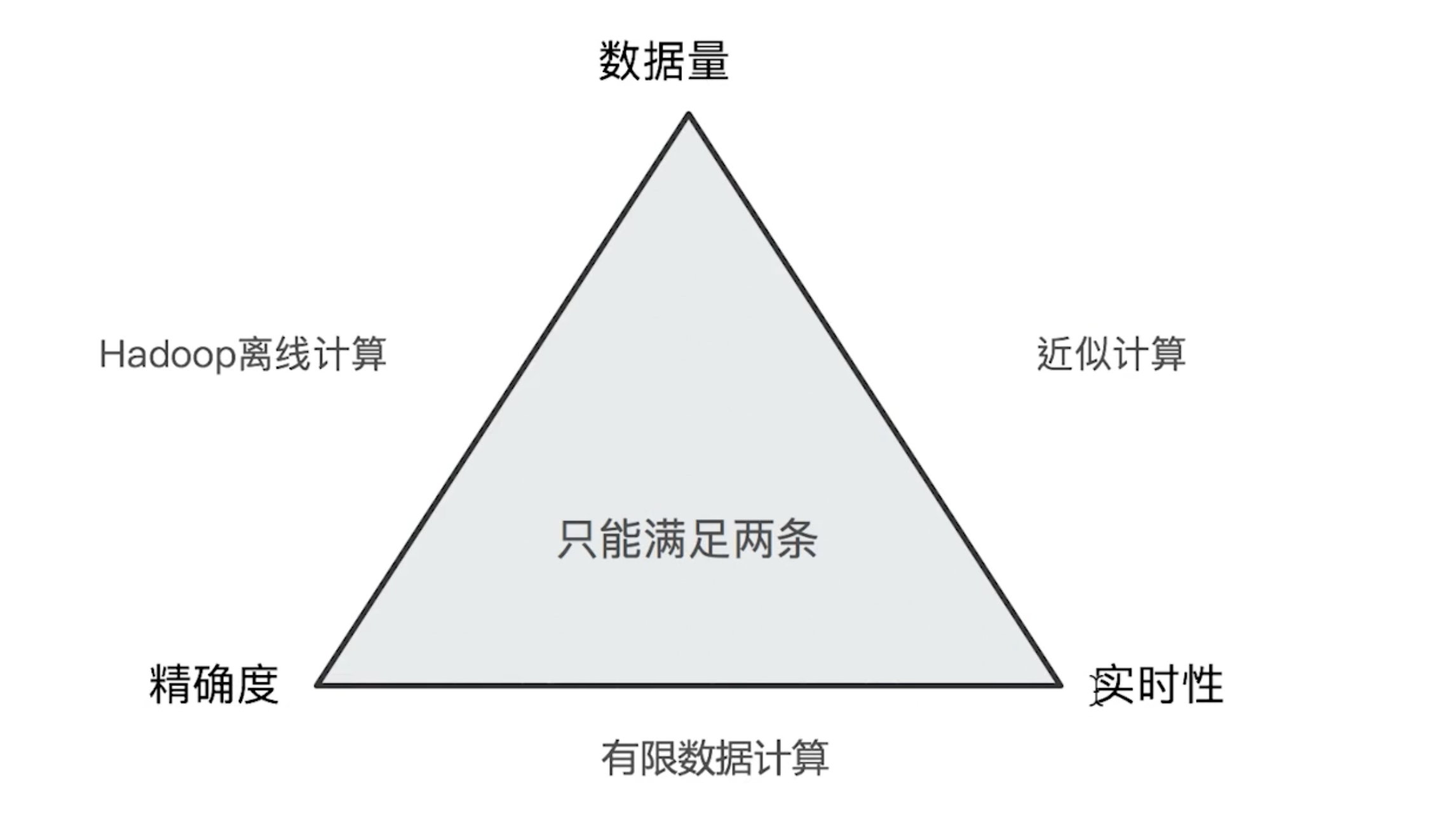
-
If the data size is small, ES works very good.
-
If the data size is big, ES will share the data on different shards, and the precision goes down.
To improve the it, there are 2 ways:
-
put all the data in one primary size.
-
increase the
shard_sizein the term aggregation.
The terms aggregation fetches more than the top size terms from each shard. It fetches the top shard_size terms, which defaults to size * 1.5 + 10.
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"<a-name>": {
"terms": {
"field": "someKeyword",
"size": 3,
"shard_size": 10 // the size of data the ES will fetch on each shard
}
}
}
}