R Basic types
-
Function:
Functions are a body of reusable code used to perform specific tasks in R.
Tpying
?before a function can show the documents of the function. i.e.?print() -
Variable:
A variable is a representation of a value in R that can be stored for use later during programming.
Variables can also be called objects.
A variable name should start with a letter and can also contain numbers and underscores.
-
Comment:
A comment must start with
#. -
Data Type:
There are number, string, date, datetime, etc. To asign a data to a variable:
first_var <- "test" -
Vector:
A vector is a group of data elements of the same type stored in a sequence in R.
vec_1 <- c(1, 2, 3) -
Pipe:
A pipe is a tool in R for expressing a sequence of multiple operations, represented with
%>%. -
Factor:
Factors store categorical data in R where the data values are limited and usually based on a finite group like country or year.
Atomic vectors
A vector that contains ONLY ONE type of data.
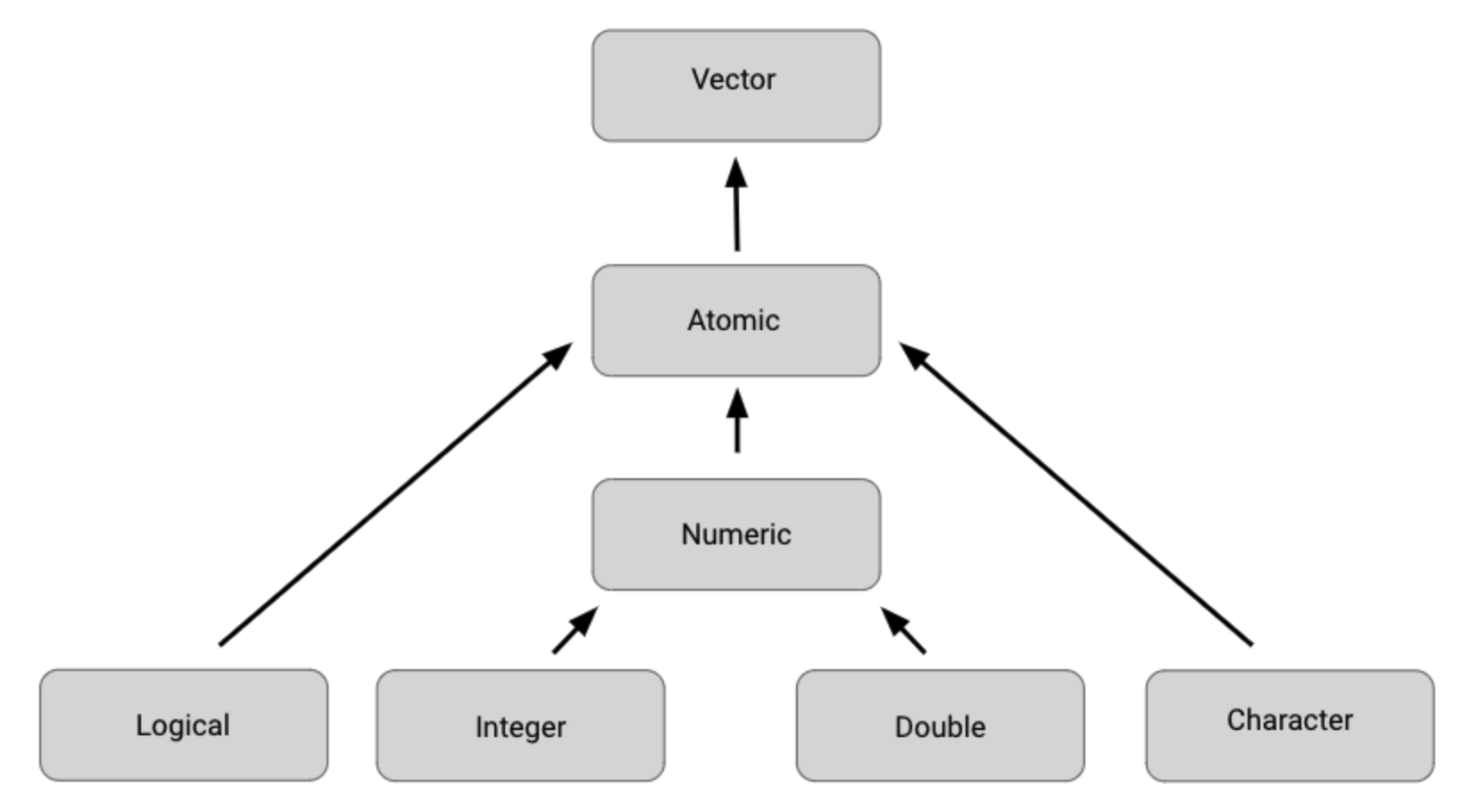
To create a vector:
- double vector:
c(2.5, 48.5, 101.5) - integer vector:
c(1L, 5L, 15L) - character vector:
c(“Sara” , “Lisa” , “Anna”) - logical vector:
c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE)
Naming vectors
x <- c(1, 3, 5)
names(x) <- c("a", "b", "c")
Now, R shows that the first element of the vector is named a, the second b, and the third c.
List
Lists are different from atomic vectors because their elements can be of any type.
Determining the structure of lists
str() shows the structure of a list.
Naming lists
list('Chicago' = 1, 'New York' = 2, 'Los Angeles' = 3)
Dates and times in R
In R, there are three types of data that refer to an instant in time:
- A date:
2016-08-16 - A time within a day:
20:11:59 UTC - a datetime:
2018-03-31 18:15:48 UTC
To get current date and datetime:
-
today(): current date -
now(): current datetime
Converting from strings:
ymd("2021-01-20")ymd_hms("2021-01-20 20:11:59")
Data frames
Data frames are the most common way of storing and analyzing data in R.
A data frame is a collection of columns–similar to a spreadsheet or SQL table.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when you are working with data frames:
- Columns should be named.
- Data frames can include many different types of data, like numeric, logical, or character.
- Elements in the same column should be of the same type.
Files
dir.createfunction to create a new folderfile.createfunction to create a new filefile.copyfunction to copy a file to the destinationunlinkfunction to delete a file
Matrix
A matrix is a two-dimensional collection of data elements.
-
matrix(c(3:8), nrow = 2):3 4 5 6 7 8 -
matrix(c(3:8), ncol = 2):3 6 4 7 5 8