Insufficient data
Types
- Data from only one source
- Data that keeps updating
- Outdated data
- Data that's geographically-limited
Ways to address insufficient data
- identify trends with the available data
- wait for more data if time allows
- talk with stakeholders and adjust your objective
- look for a new data set.
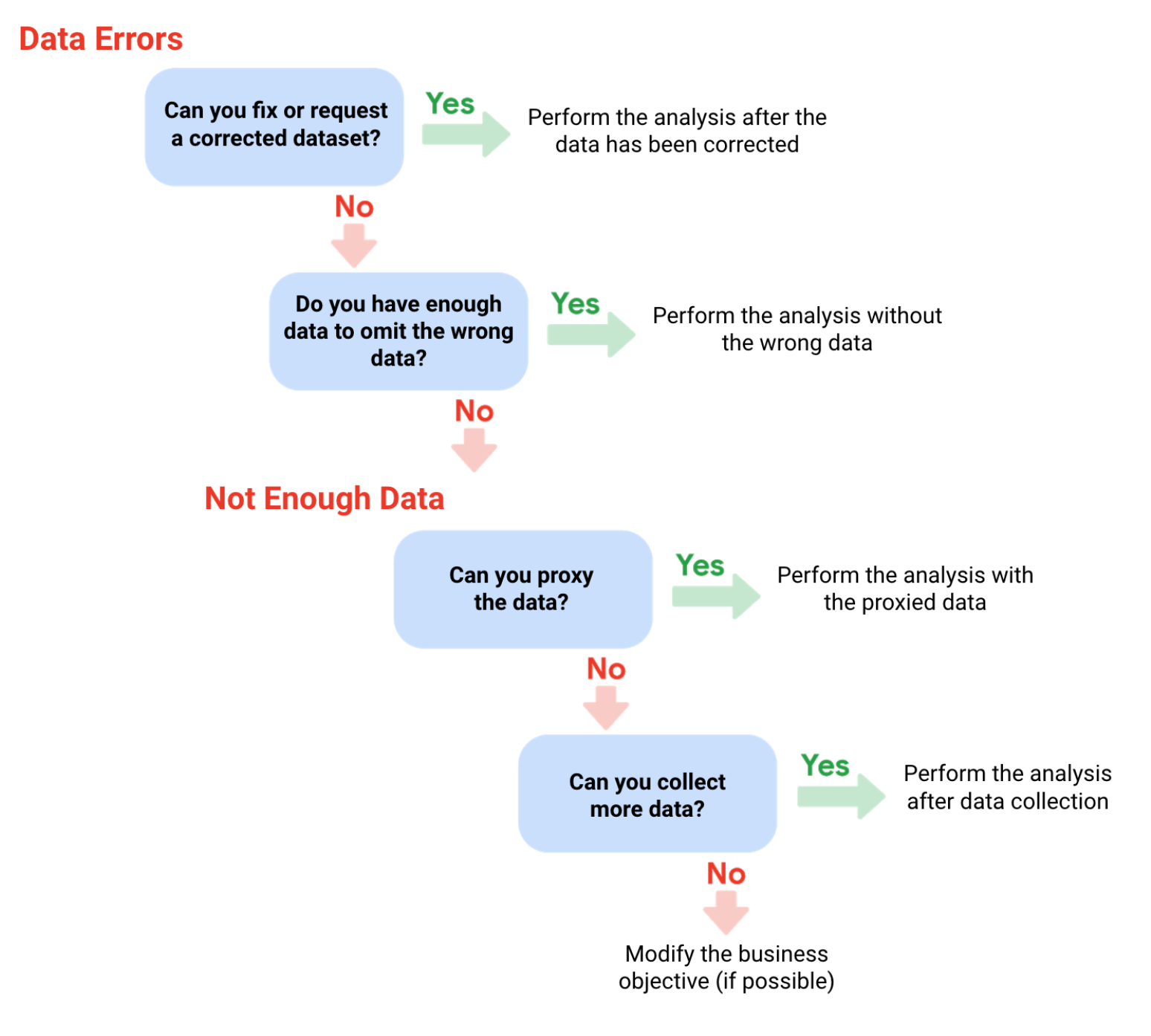
Deal with data errors
Sample Size (Sample)
A part of a population that's representative of the population.
The goal is to get enough information from a small group within a population to make predictions or conclusions about the whole population.
Terms
| Terminology | Definitions | | ------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | Population | The entire group that you are interested in for your study. | | Sample | A subset of your population. | | Margin of error | This difference is between the sample’s results and population's results. | | Confidence level | How confident you are in the survey results. | | Confidence interval | The range of possible values that the population’s result would be at the confidence level of the study. This range is the sample result +/- the margin of error. | | Statistical significance | The determination of whether your result could be due to random chance or not. The greater the significance, the less due to chance. |
Things to remember when determining the size of your sample
-
Don’t use a sample size less than 30.
It has been statistically proven that 30 is the smallest sample size where an average result of a sample starts to represent the average result of a population.
-
The confidence level most commonly used is 95%, but 90% can work in some cases.