Data classification
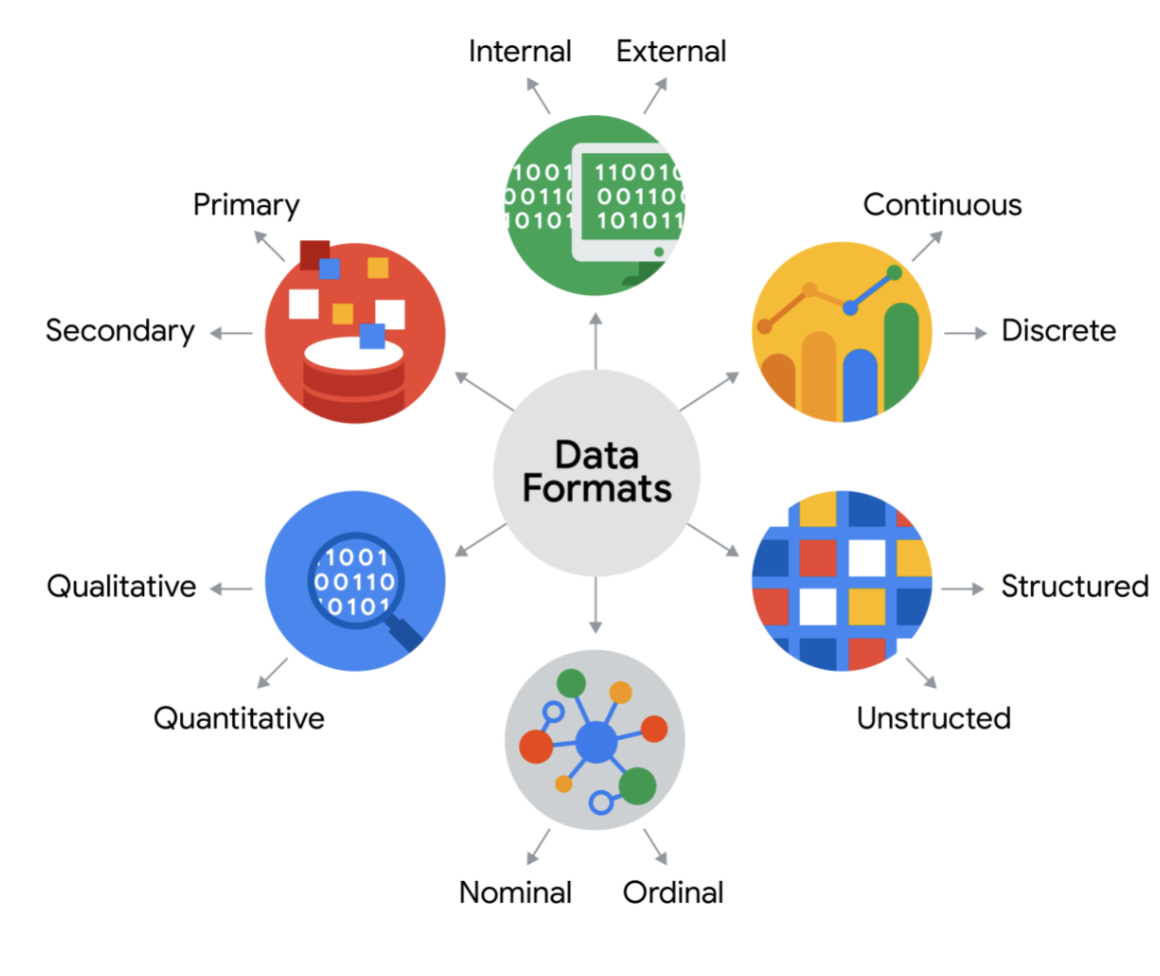
As dicussed before, data can be split into qualitative and quantitative.
The quantitative can be classfied in 2 different types: discrete and continuous.
Discrete data vs Continuous data
-
Discrete data: It can be counted and have a limited number of values.
-
Continuous data: It can be measured using a timer, and its value can be shown as a decimal with several places.
Nominal data vs Ordinal data
-
Nominal data: It is a type of qualitative data that's categorized without a set order.
-
Ordinal data: It's a a type of qualitative data with a set order or scale.
Internal data vs External data
The internal data that lives within a company's own systems.
Structured data vs Unstructured data
-
Structured data: It is data that's organized in a certain format, such as rows and columns. It's easier to store, search and analyze.
-
Unstructured data: This is data that is not organized in any easily identifiable manner.
Data model
Data modeling is the process of creating diagrams that visually represent how data is organized and structured. These visual representations are called data models.
Data model that is used for organizing data elements and how they relate to one another.
Data models help to keep data consistent and provide a map of how data is organized.
Data element
They're pieces of information, such as people's names, account numbers, and addresses
Levels of data modeling
-
Conceptual data modeling gives a high-level view of the data structure, such as how data interacts across an organization.
-
Logical data modeling focuses on the technical details of a database such as relationships, attributes, and entities.
-
Physical data modeling depicts how a database operates. A physical data model defines all entities and attributes used.
Data-modeling techniques
-
Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
ERDs are a visual way to understand the relationship between entities in the data model.
-
Unified Modeling Language (UML)
UML diagrams are very detailed diagrams that describe the structure of a system by showing the system's entities, attributes, operations, and their relationships.
Data types
A data type is a specific kind of data attribute that tells what kind of value the data is.
Data types in the spreadsheet
-
Number
-
String
-
Boolean
Data types in the database
-
Records: rows
-
Fields: columns
Wide data vs Long data
Wide data
Every data subject has a single row with multiple columns to hold the values of various attributes of the subject.
Wide data lets you easily identify and quickly compare different columns.
It's used for:
-
Creating tables and charts with a few variables about each subject
-
Comparing straightforward line graphs
Long data
Long data is data in which each row is one time point per subject, so each subject will have data in multiple rows.
It's used for:
-
Storing a lot of variables about each subject. For example, 60 years worth of interest rates for each bank
-
Performing advanced statistical analysis or graphing
Data transformation
Data transformation is the process of changing the data’s format, structure.
Data transformation usually involves:
-
Adding, copying, or replicating data
-
Deleting fields or records
-
Standardizing the names of variables
-
Renaming, moving, or combining columns in a database
-
Joining one set of data with another
-
Saving a file in a different format. For example, saving a spreadsheet as a comma separated values (CSV) file.
Why transform data?
Goals for data transformation might be:
-
Data organization: better organized data is easier to use
-
Data compatibility: different applications or systems can then use the same data
-
Data migration: data with matching formats can be moved from one system to another
-
Data merging: data with the same organization can be merged together
-
Data enhancement: data can be displayed with more detailed fields
-
Data comparison: apples-to-apples comparisons of the data can then be made